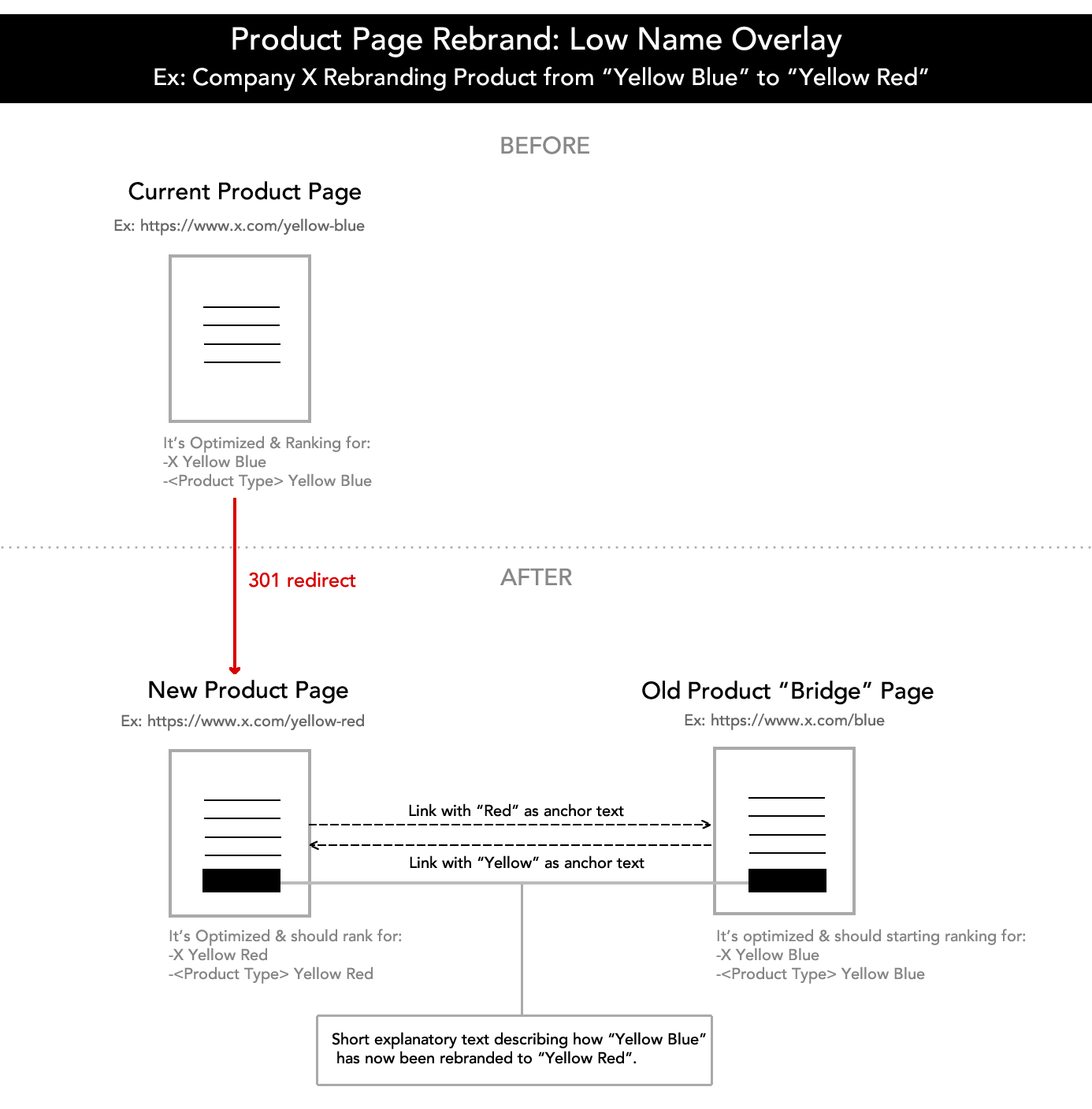
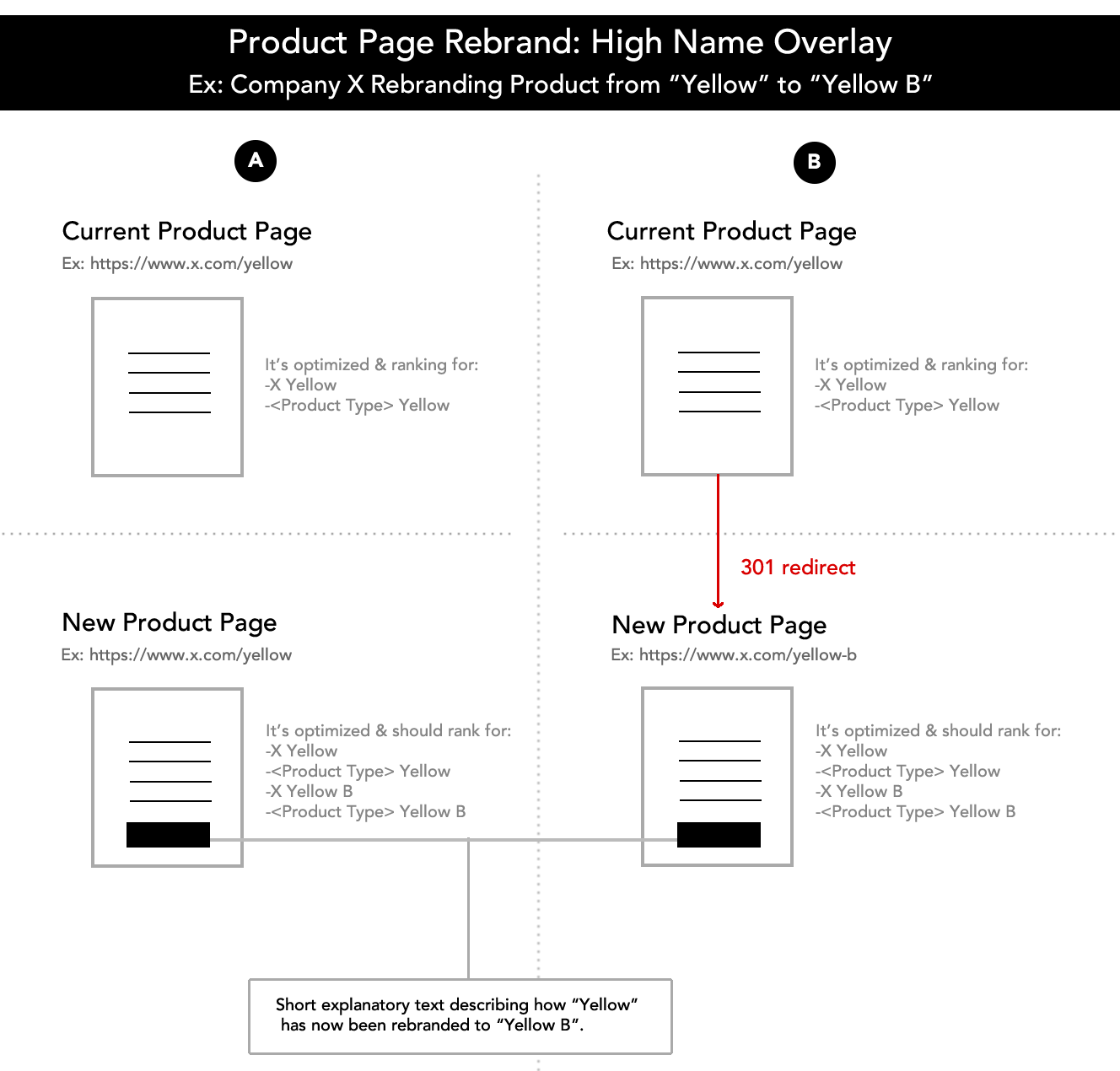
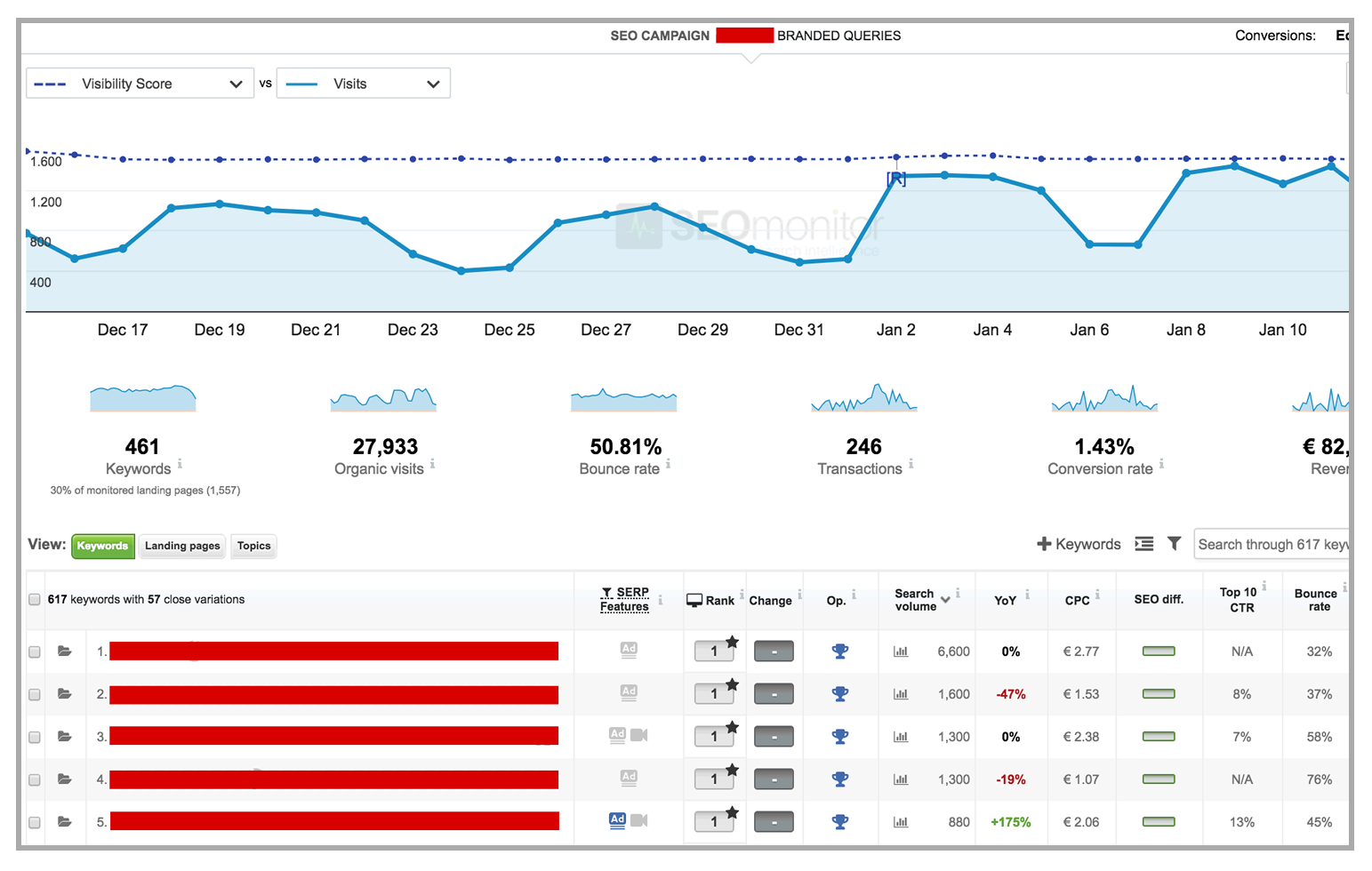
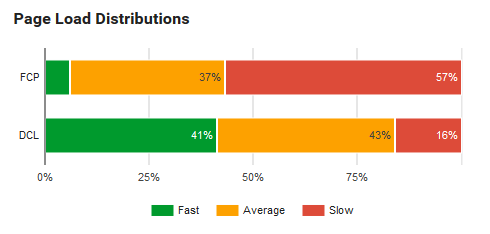
It’s imperative for SEM managers to have a broad toolset at their disposal at all times.
When it comes to free PPC tools, there are
so many great free resources available.
After
crowdsourcing a few dozen suggestions from my LinkedIn and Twitter
networks, as well as my team, I came to an undeniable conclusion:
everyone is trying to do the same thing in different ways.
The old Abraham Maslow adage of “If your only tool is a hammer, every problem looks like a nail,” comes to mind.
What
follows is a comprehensive resource guide to free and freemium PPC
tools, organized by task or goal, with tips and tricks to make the most
of each tool.
Keyword Research Tools
Free
Google + Bing Keyword Planners
A lot of people don’t like the keyword tool because the data can be anywhere from inaccurate to outright wrong.
However, I love the keyword planners to death, even if the data can be a bit suspect.
You have to take them for what they are. They’re designed for expanded ideation.
When you put keywords in for ideas, the tools fire off matches the same way pure broad match might work.
Google
and Bing’s keyword planners aren’t perfect, but can plant amazing seed
ideas for campaigns and ad groups. The decent (but not perfect) volume
estimates are a bonus.
A few tips:
- Use the volume
estimates as directional data, not as absolutes. Set your base bids
based on what you can afford, not what the tools say the average is.
- I’ve
always used a 1,000 monthly searches estimate as a secondary threshold
to segment ad groups. This still holds true as a good proxy when search
intent + messaging are too close to call.
- In general, things
with no volume estimates will get tagged with low search volume and
likely won’t show. Its fine to include them in the account, but be
careful of ad group sculpting (negating exact from broad or phrase).
This may prevent the LSV queries from ever showing.
- Don’t get too precise with regions. Estimates lose their utility when you go beyond State or Province level.
Google Search Console + Google Analytics
You can get a decent amount of organic query data out of
Google Search Console, which can help flesh out your campaigns and fill in gaps.
Google Analytics can give limited organic search data, but the real value comes from analyzing your on-site searches.
Be careful however, that your PPC doesn’t wind up stealing market share from organic.
Search Suggestion Tools
Keywordtool.io,
UberSuggest.io and
Soovle all do loosely the same thing – they scrape search suggestions from various engines, each with varying degrees of completeness.
Each has their own distinct advantages/disadvantages. It’s worth toying with each to ensure you have complete coverage.
- UberSuggest has the most comprehensive pull from Google, but nowhere else. Plus you can export the data.
- Keyword
Tool has a few more options (including Bing/Amazon/eBay), but it
doesn’t seem to generate quite as robust a list as Uber. Data is also
exportable.
- Soovle allows you to pick from every engine under the sun, but limits the results it shows. Great for finding super long-tail terms to target search partner-heavy terms.
Answer The Public
is a humanized version search suggest and the closest thing I’ve seen
to replicating the Google Wonder Wheel (RIP). Enter your base word or
phrase, and it’ll spring off into natural language queries.
It’s
more valuable as a content/landing page/ad copy development too than a
purebred keyword tool. Plus it’s got a handsome old man with a nice
sweater on it.
Freemium
If anyone finds a paid/freemium keyword research tool that’s worth it, let me know.
Honorable Mentions
Keywords Everywhere is a Chrome extension that shows volume + competition in the search bar.
KW Finder is another suggest-based tool including a competitiveness metric.
Keyword Wrapper formats your builds to include BMM/phrase/exact match. I’m an Excel-first guy, but if you want a match type wrapper it’s here.
BigQuery to Sheets de-samples analytics data. I haven’t personally used it but it was recommended by a few.
PPC Competitive Analysis Tools
If you’re using a competitive analysis tool to find competitive spend, you’re doing it wrong.
The estimator tools all operate (roughly) by scraping the SERP and reporting back on what they can see.
They triangulate via estimates in Keyword Planners to get spend estimates.
If you must guess what others are spending, run yourself through the tools and use competitive estimates as a proportion.
You’ll be wrong, though.
Free
Auction Insights
Auction Insights from Bing + Google are the best competitive analysis tools you’ll find.
They’re free in the sense that there’s no monthly fee, but expensive as they’ll only show competitive data relative to your own.
Bear in mind auction insights pull data at the auction level.
If you pull data on broad match terms or shopping campaigns, you’ll have a far less accurate picture.
Sticking to exact match terms will give the clearest insights.
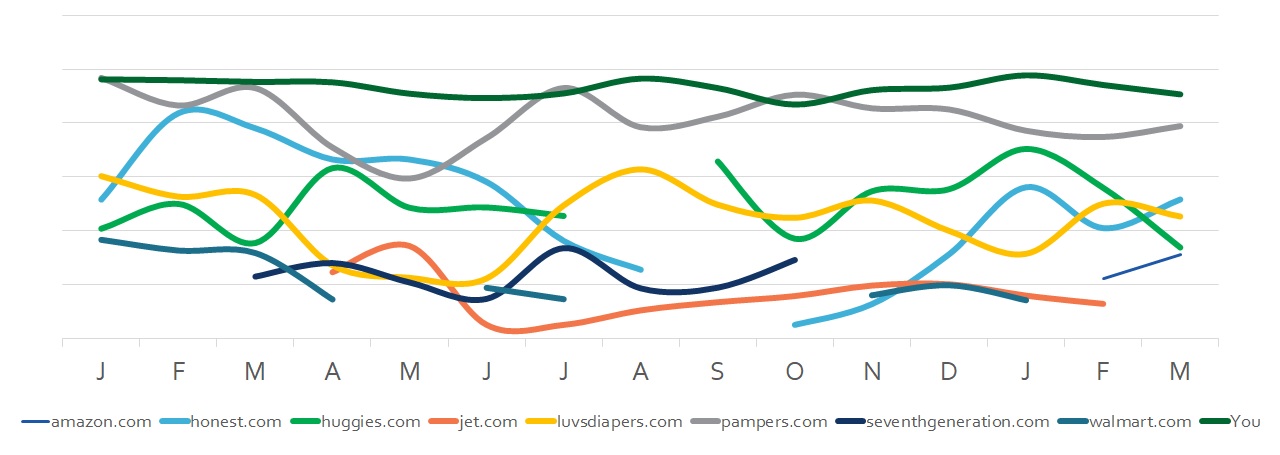
Remember to segment by time to see how their strategy evolves!
Freemium
SpyFu/iSpionage/KeywordSpy/SEMrush
Each of these SERP scraping tools give you a bit of insight for free, but with investment comes far better data.
I’m oversimplifying here, but the baseline use of each is similar.
You can see what ads appeared over time and for what keywords. The differentiation comes from the added “bells and whistles.”
SEMRush + SpyFu are the most robust (and thus, most expensive after free trial) but they feature the most complete dataset.
AdBeat
This tool accomplishes much of the same for display.
You can get some competitive data for free, but robust reporting will cost you.
Bidding + Campaign Management Tools
Free
AdWords Scripts
Don’t get scared of scripts because you don’t have a coding background.
There’s a myriad of free resources out there to help educate you.
Checking landing pages, adjusting for anomalies or pausing a campaign that goes haywire should be simply automated.
A few of my favorite script libraries include:
There’s also the good old-fashioned
Google Developer’s Guide.
Buyer beware – AdWords scripts will time out after 30 minutes, and can only touch 250,000 entities per go.
Make sure you have controls in place lest your script only touch part of the account.
Automated Rules from Google + Bing
Automated
Rules from Google + Bing are both fantastic for executing simple tasks
like pausing ads at the end of a sale or boosting bids to first page
recommendations.
If your account is more complex, you can use labels to help guide the rules.
Bidding Tools from Google + Bing
By the same token, Bidding Tools from both of the engines are effective.
I’ve heard a myriad of complaints and conspiracy theories around these – trusting the fox to guard the henhouse, if you will.
Remember, it’s in the engines best interests for your advertising to perform well!
Each of the engine bidding tools has their own strengths and weaknesses.
As a general rule, you can trust the engines to make smart decisions with correct data.
A significant lot of offline information or a complicated sales process can diminish UI-based bidding tools.
However, if all of the data you’d need is within the interfaces, give their bidding tools a try.
Make sure to set CPC caps where applicable, however, so the tools don’t get
too excited.
Freemium/Affordable (But Worth It)
There are a million and one bidding platforms available.
I’m not going to get into a debate for which is best, and they are most definitely not free.
On a smaller scale, tools like
Adalysis can make your PPC lives significantly easier by automating account checks and ad tests.
Optymzer is another great option in the same vein.
Both feature a 14-day free trial to see if they’re a fit.
Reporting + Data Visualization
Free
Google Data Studio
Google Data Studio is glorious, plain and simple.
As
long as all of the data you need lives in engines or DoubleClick, it’s
easy to get things set up in a nice tidy live dashboard.
If you have any issues or any
data sources you can’t embed, there’s a robust developer community or a number of connectors available from
SuperMetrics
Chandoo and ExcelCharts
If you are an Excel person (as most of us are), you’ll need a deft hand to create more than stacked bars and bubble charts.
Chandoo.org + ExcelCharts.com are two of my favorites to better understand data visualization and to make your results sing.
Freemium/Affordable
SuperMetrics
is a comprehensive tool to get your marketing data in a single place.
It was initially developed for Google Sheets + Excel, but now can port
data directly into Data Studio.
If you can’t get things done in Data Studio, there are many options available to help.
Swydo,
ReportGarden, and
Reporting Ninja each have a variety of bonus features beyond dashboarding and basic budget management.
AdStage and
NinjaCat are a bit more robust solutions if you need complex data integration. All have free trials, and monthly fees beyond that
Audiences Insights
Free
Google Display Planner
The Google Display Planner is good at a lot of things beyond setting up a display campaign.
Drop your website in to get a view of affinity topics + interests, as well as related demographic and device browsing behavior.
These can help prioritize search campaigns and set better bid modifiers
AdWords Audience Insights
AdWords
Audience Insights can paint a clear picture of exactly who’s visiting
your site, on your CRM list, or (better yet) converting.
Facebook Audience Insights
Facebook Audience Insights will do the same, but with far greater accuracy.
Both can give a ton of information into the composition of your actual audience.
Freemium
There are a few options available for robust audience insights and behavioral analysis.
SimilarWeb (no registration required) or
Alexa (7-day
trial) grant tons of user information and paint a picture of your site
audience or that of your competitors. Both products are on the pricey
side, but you can get a good deal of information for free.
Conversion Rate Optimization
Free
Post-click optimization is a crucial tool to have in your PPC toolbelt, and the tools don’t have to cost a ton!
Google Optimize
Google Optimize is a good place to start, allowing simple site tests without heavy coding.
You
can launch A/B tests, basic multivariate tests, or re-directs to
control what a user sees without having to clone your ads a million
times.
The tool is on the basic side.
VWO and Optimizely
If your testing program expands you may want to invest a premium tool like VWO or Optimizely
.
Freemium
Much
of conversion rate optimization comes down to a basic understanding of
how the human mind and eyes work, and what draws attention.
Heat
mapping and mouse recording are both powerful methods to understand
where users go first and to help assess before and after of your CRO
tests.
HotJar
HotJar is a great heat
mapping tool product that has a limited free-forever version, though
more robust options start at $29/month.
Unbounce
If you
don’t have a strong landing page, heat mapping isn’t the best place to
start. Instead, start by developing a solid landing page for your
campaign.
Unbounce is arguably the best known (and longest
tenured) landing page tool and has a 30-day trial to get started, then
it starts at $79/month after that.
Lander
Lander is more affordable (starting at $16/month after trial), but isn’t quite as robust.
Ontrapages
You can get free-forever landing pages from Ontrapages
, albeit with a little branding until you upgrade.
Bonus Things I Love
Focus and Productivity
A lot of us work in open offices now which are proven to be counterproductive for pretty much anything besides meetings.
I recommend the
Music For Office Workers playlist
series from Drowned in Sound (note: need to sign up/sign in to Spotify
to use). It helps drown out distractions, replacing them with beautiful
ambient + classical music. Pair it with an
Audioengine D1 and your favorite headphones for extra high-quality focus tunes.
For those who are more of the ambient noise camp, check out
Noisli.
It’s
important to remember the human brain isn’t exactly a finely-tuned
focus machine – we only have a certain capacity before we lose
effectiveness,
especially the millennial brain.
I’m a huge proponent of the Pomodoro method (3-5 minute breaks every 25-30 minutes).
Marinara
is a simple extension tells you when it’s time to take a break and look
at something else for a few minutes to clear your head. It’s good for
your eyes, too!
Project Management
Project
management is one thing I see people struggle with as they grow in
their careers. Nothing is more challenging than putting together reports
and forgetting what you did.
I love
Trello to keep track of long-term projects across teams.
For a more robust solution,
FreedCamp acts as a freemium version of Basecamp. It’s not as complete but will suffice in many scenarios.
That said, a well-developed
Google Sheet can go a long way.
Reference:
https://www.searchenginejournal.com/essential-free-ppc-tools/232971/